-
1 button lamp
pilot lamp — контрольная лампочка; сигнальная лампа
English-Russian dictionary of Information technology > button lamp
-
2 button lamp
1) Военный термин: кнопочная лампа2) Телекоммуникации: кнопочная лампочка -
3 button lamp
-
4 button lamp
English-Russian dictionary of modern telecommunications > button lamp
-
5 push-button lamp
-
6 button-barrel lamp
-
7 illuminated push-button
кнопка с подсветкой
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
нажимная кнопка с сигнализацией
Аппарат, в корпус которого встроена сигнальная лампа.
[ ГОСТ 50030.5.1-2005]EN
illuminated push-button
a push-button incorporating a signalling lamp in the button
[IEC 60947-5-1, ed. 3.0 (2003-11)]FR
bouton-poussoir lumineux
bouton-poussoir dans le bouton duquel est incorporée une lampe de signalisation
[IEC 60947-5-1, ed. 3.0 (2003-11)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- выключатель кнопочный, кнопка
Обобщающие термины
EN
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > illuminated push-button
-
8 push-to-test button
-
9 head
головка (напр. болта); шляпка (напр. гвоздя); днище (поршня) (рис. 3,4) ; головка блока цилиндров (двигателя); напор (жидкости); бабка (токарного станка); боёк (молота); литник; насадка (верхняя или передняя); направление; руководитель; глава; головная часть; передняя часть; II осаживать головку; высаживать головку; возглавлять; руководить; II головной; главный; ведущий
- head cushion
- head fall
- head lamp
- head lamp bulb
- head lamp case
- head lamp case rim
- head lamp dimmer
- head lamp door
- head lamp door latch
- head lamp door socket
- head lamp door spring
- head lamp lens
- head lamp lower beam
- head lamp reflector
- head lamp support
- head lamp swivel
- head lamp tester
- head lamp upper beam
- head lamp with antivibration device
- head light
- head lighting
- head of delivery
- head of rivet
- head of water
- head on turbine
- head-on view
- head resistance
- head rest
- head room
- head way
- head wind
- ball head
- bar head- casing head - caulked head - connecting-rod head - countersunk head - cubic head- cup head- detector head- die head- double-radius button head - drive head of a conveyer - filister binding head - finned cylinder head - flaming head - flattened-round head- gib head- hex head - hexagon head - horse's head - hydraulic head - hydraulic pressure head - index head - instrument head - integral cylinder head - knife head ball - knurled head - lentil head - lug head - manipulator head - manufactured head of rivet - milled head - movable head - multi-spindle head - mushroom head - nigger head - oval head - oven binding head - pan head - Philips head - pinched head - piston head - pressure head - primary head - rag head - ram head - ripping head - riveted-over head - rope-type head - round head - rounded countersunk head - screw head - set head - shake head - shear head - shower head - sickle head - slotted head - snap head - socket head - solid head - spindle head - spiral head - spray head - square head - steep head - steeple head - steering head - straight-base button head - strap head - suction head - swaged head - T-head - tapping head - tension head of a conveyer - thinner head - thrashing cylinder head - thread head - tommy head - upset head - valve head - washer head - winged head
; головка блока цилиндров (двигателя); напор (жидкости); бабка (токарного станка); боёк (молота); литник; насадка (верхняя или передняя); направление; руководитель; глава; головная часть; передняя часть; II осаживать головку; высаживать головку; возглавлять; руководить; II головной; главный; ведущий
- head cushion
- head fall
- head lamp
- head lamp bulb
- head lamp case
- head lamp case rim
- head lamp dimmer
- head lamp door
- head lamp door latch
- head lamp door socket
- head lamp door spring
- head lamp lens
- head lamp lower beam
- head lamp reflector
- head lamp support
- head lamp swivel
- head lamp tester
- head lamp upper beam
- head lamp with antivibration device
- head light
- head lighting
- head of delivery
- head of rivet
- head of water
- head on turbine
- head-on view
- head resistance
- head rest
- head room
- head way
- head wind
- ball head
- bar head- casing head - caulked head - connecting-rod head - countersunk head - cubic head- cup head- detector head- die head- double-radius button head - drive head of a conveyer - filister binding head - finned cylinder head - flaming head - flattened-round head- gib head- hex head - hexagon head - horse's head - hydraulic head - hydraulic pressure head - index head - instrument head - integral cylinder head - knife head ball - knurled head - lentil head - lug head - manipulator head - manufactured head of rivet - milled head - movable head - multi-spindle head - mushroom head - nigger head - oval head - oven binding head - pan head - Philips head - pinched head - piston head - pressure head - primary head - rag head - ram head - ripping head - riveted-over head - rope-type head - round head - rounded countersunk head - screw head - set head - shake head - shear head - shower head - sickle head - slotted head - snap head - socket head - solid head - spindle head - spiral head - spray head - square head - steep head - steeple head - steering head - straight-base button head - strap head - suction head - swaged head - T-head - tapping head - tension head of a conveyer - thinner head - thrashing cylinder head - thread head - tommy head - upset head - valve head - washer head - winged head -
10 ABS
= AntiBlock Systemантиблокировочная система тормозов в автомобиле (АБС); противозаклинивающее тормозное устройство- Anti-locking Braking System - Air Bag System - Automatic Block Signal - Antiskid Brake System - Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene - ABS brakes - AntiBlock System brakes - ABS handle - Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene handle - ABS hydraulic fluid reservoir - AntiBlock System hydraulic fluid reservoir - ABS indicator lamp - AntiBlock System indicator lamp - ABS module - AntiBlock System module - ABS override button - AntiBlock System override button - ABS part - AntiBlock System part - ABS resin - Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene resin - ABS unit - AntiBlock System unit - ABS warning light - AntiBlock System warning light - combined ABS - AntiBlock System - screwdriver with ABS-handle -
11 electronic microprocessor-based release
микропроцессорный расцепитель
электронный расцепитель
-
[Интент]Микропроцессорный (электронный) расцепитель позволяет очень точно настроить параметры защиты и обеспечить селективность относительно расположенных ниже автоматических выключателей.
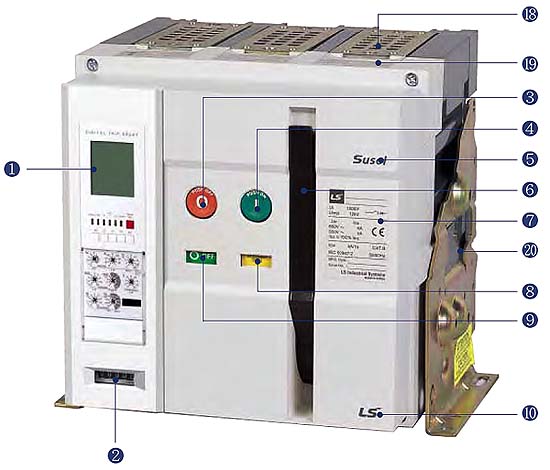

Рис. LS Industrial Systems
Стационарный автоматический выключатель:
1- Микропроцессорный расцепитель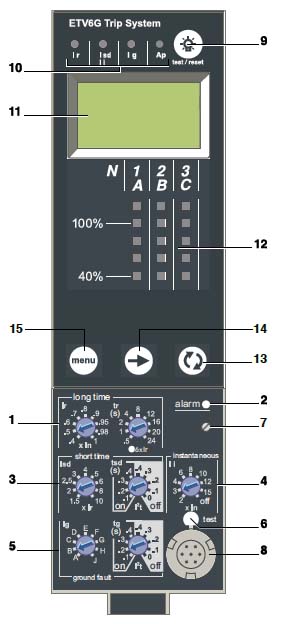
Микропроцессорный расцепитель
Рис. Schneider Electric1 Long-time threshold and tripping delay
1. Уставка тока защиты с длительной задержкой срабатывания и задержка срабатывания.
2 Overload alarm (LED) at 1,125 Ir.
2. Светодиодный индикатор перегрузки превышающей 1,125 Ir.
3 Short-time pick-up and tripping delay.
3. Уставка тока защиты с кратковременной задержкой срабатывания и задержка срабатывания.
4 Instantaneous pick-up.
4. Уставка тока защиты мгновенного срабатывания
5 Earth-fault pick-up and tripping delay.
5. Уставка тока защиты от замыкания на землю и задержка срабатывания
6 Earth-fault test button.
6. Кнопка проверки срабатывания при замыкании на землю
7 Long-time rating plug screw.
7. Калибратор защиты с длительной задержкой срабатывания
8 Test connector.
8. Разъем для тестирования
9 Lamp test, reset and battery test.
9. Кнопка сброса состояния срабатывания и проверки индикаторов и гальванического элемента
10 Indication of tripping cause.
10. Индикация причины срабатывания
11 Digital display.
11. Символьный экран
12 Three-phase bargraph and ammeter.
12. Светодиодные шкалы индикации токов фаз А, В и С
13 Navigation button “quick View”.
13. Кнопка быстрого просмотра
14 Navigation button to view menu contents.
14. Кнопка перемещения по меню
15 Navigation button to change menu
[Schneider Electric]15. Кнопка перехода от одного меню к другому
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- выключатель автоматический
- расцепитель, тепловое реле
Классификация
>>>Синонимы
EN
Примечание(1) - термин Schneider ElectricАнгло-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > electronic microprocessor-based release
-
12 trip system (1)
микропроцессорный расцепитель
электронный расцепитель
-
[Интент]Микропроцессорный (электронный) расцепитель позволяет очень точно настроить параметры защиты и обеспечить селективность относительно расположенных ниже автоматических выключателей.

Рис. LS Industrial Systems
Стационарный автоматический выключатель:
1- Микропроцессорный расцепитель
Микропроцессорный расцепитель
Рис. Schneider Electric1 Long-time threshold and tripping delay
1. Уставка тока защиты с длительной задержкой срабатывания и задержка срабатывания.
2 Overload alarm (LED) at 1,125 Ir.
2. Светодиодный индикатор перегрузки превышающей 1,125 Ir.
3 Short-time pick-up and tripping delay.
3. Уставка тока защиты с кратковременной задержкой срабатывания и задержка срабатывания.
4 Instantaneous pick-up.
4. Уставка тока защиты мгновенного срабатывания
5 Earth-fault pick-up and tripping delay.
5. Уставка тока защиты от замыкания на землю и задержка срабатывания
6 Earth-fault test button.
6. Кнопка проверки срабатывания при замыкании на землю
7 Long-time rating plug screw.
7. Калибратор защиты с длительной задержкой срабатывания
8 Test connector.
8. Разъем для тестирования
9 Lamp test, reset and battery test.
9. Кнопка сброса состояния срабатывания и проверки индикаторов и гальванического элемента
10 Indication of tripping cause.
10. Индикация причины срабатывания
11 Digital display.
11. Символьный экран
12 Three-phase bargraph and ammeter.
12. Светодиодные шкалы индикации токов фаз А, В и С
13 Navigation button “quick View”.
13. Кнопка быстрого просмотра
14 Navigation button to view menu contents.
14. Кнопка перемещения по меню
15 Navigation button to change menu
[Schneider Electric]15. Кнопка перехода от одного меню к другому
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- выключатель автоматический
- расцепитель, тепловое реле
Классификация
>>>Синонимы
EN
Примечание(1) - термин Schneider ElectricАнгло-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > trip system (1)
-
13 illuminated pushbutton
нажимная кнопка с сигнализацией
Аппарат, в корпус которого встроена сигнальная лампа.
[ ГОСТ 50030.5.1-2005]EN
illuminated push-button
a push-button incorporating a signalling lamp in the button
[IEC 60947-5-1, ed. 3.0 (2003-11)]FR
bouton-poussoir lumineux
bouton-poussoir dans le bouton duquel est incorporée une lampe de signalisation
[IEC 60947-5-1, ed. 3.0 (2003-11)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- выключатель кнопочный, кнопка
Обобщающие термины
EN
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > illuminated pushbutton
-
14 control
управление; органы управления; система управления; блок управления; орган настройки; проверка; надзор; воздействие; осмотр; механизм (подачи); регулирование; регулирующее устройство; орган регулировки; профилактические мероприятия; власть; контрольное управление; pl. органы управления; рычаги управления; ручки настройки; II управлять (процессом); регулировать; проверять; распоряжаться; II регулировочный; контрольный- control by fuel delivery - control by measurement - control cab - control chart - control check - control circuit - control clutch - control coefficient - control combination - control command - control console - control crank - control current - control Curvic coupling - control drive - control equipment - control failure - control force - control gauge - control gear - control handle - control housing - control housing socket - control hydraulic valve - control joint - control knob - control lamp - control lever - control line - control panel - control pedal - control pinion - control post - control rack - control rod - control room - control set - control stand - control switch - control system - control tender - control the traffic - control unit - control valve - control wire - acceleration control - air fuel control - air mixture control - air-operated control - alarm control switch - all speed control - aneroid control - assisted control - beam control - boom kick-out control level - boom shockless control switch - bucket control level - button control - chain control - choke control - close loop control system - clutch control - combustion control - constant service control - constant torque control - cycling control - depth control stop - differential lock control valve - direct control - direction control lever - directional control lever - distant control - draught control - eccentric control - electromagnetic control - electronic control - electronic control module - electronic control suspension system - electronic control with single and group operations - emission control system - ECS - engine controls - federal emission control standards - fine control - fine control hole - flow control valve - fuel control cable - fuel control dial - fuel control lever - fuel control linkage - fuel control rod - fuel-flow control - fuel ratio control - gear control - gearshift control lever - hand control - height control - hoist control - humidity control - hydraulic control - hydraulic control linkage - hydraulic control valve - hydraulic depth control - hydraulic height control - idle control - knob control - lever control - light-touch steering control - manual control - main control valve - mixture control - mode control valve - negative control valve - overheat control - pneumatic control - power control - power-assisted control - press-button control - pressure control - pulse control - push-button control - quality control - quality power level control - remote control - remote position control - resistance control - rheostatic control - rod control - safety controls - semi-automatic control - sensitivity time control - STC - sight control - snow-drift control - spark control - speed control - stepless control - stepped control - street traffic control - throttling control - time-gain control - viscosity control - wheel control - wireless control - Wool Control -
15 back up
= back up backup III1) давать задний ход; двигаться в обратном направлении; поддерживать; подпирать2) запасной; запасный; резервный; дублирующий- backup control - back - back-and-forth bending test - back and forward - back band - back bias - back block - back brace - back button - back checking - back clearance - back cone - back contact - back country - back current - back cushion - back digger - back draft - back drive - back driving - back dumping - back eccentric - back edge - back electromotive force - back elevation - back EMF - back filler - back fire - back flash - back flow - back flush - back flushing - back force - back gear - back-geared - back guide bar - back-guy - back haul - back header - back heating - back hoe - back hoe bucket - back hoe control valve - back impact - back jamming - back kick - back lamp - back lash - back leg - back light - back light frame - back line - back loading - back mirrow - back motion - back nut - back of bearing - back of cam - back off - back of piston ring - back of seat - back of wedge - back out - back pad - back panel - back pedalling brake - back pitch - back plate - back play - back pressure - back pressure manometer - back pressure of exhaust - back pressure regulator - back-pressure valve - back priming - back rest - back-rest adjustment - back ridge - back road - back rolling - back running - back seat - back set - back-set - back shaft - back-shot - back shovel - back sight - back single-cross seat - back slope - back sloper - back sloping - back spring - back sputtering - back squb - back stay - back stop - back sriking of spark - back stroke - back suction - back tilting table - back-to-back - back-to-back test - back transfer - back-up lamp - back-up roll bearer - back-up buzzer - back-up spring - back-up washer - back upthrow bolt cam - back valve - back visibility - back wall - back washing - back wearing ring - back window - buffalo-back - exhaust back pressure - filter back-flush porrt - fold-back seat - folding back - high-back seat - offset back hoe - pack-back cab - ring-back clearance - seat back - throttle back -
16 Edison, Thomas Alva
SUBJECT AREA: Architecture and building, Automotive engineering, Electricity, Electronics and information technology, Metallurgy, Photography, film and optics, Public utilities, Recording, Telecommunications[br]b. 11 February 1847 Milan, Ohio, USAd. 18 October 1931 Glenmont[br]American inventor and pioneer electrical developer.[br]He was the son of Samuel Edison, who was in the timber business. His schooling was delayed due to scarlet fever until 1855, when he was 8½ years old, but he was an avid reader. By the age of 14 he had a job as a newsboy on the railway from Port Huron to Detroit, a distance of sixty-three miles (101 km). He worked a fourteen-hour day with a stopover of five hours, which he spent in the Detroit Free Library. He also sold sweets on the train and, later, fruit and vegetables, and was soon making a profit of $20 a week. He then started two stores in Port Huron and used a spare freight car as a laboratory. He added a hand-printing press to produce 400 copies weekly of The Grand Trunk Herald, most of which he compiled and edited himself. He set himself to learn telegraphy from the station agent at Mount Clements, whose son he had saved from being run over by a freight car.At the age of 16 he became a telegraphist at Port Huron. In 1863 he became railway telegraphist at the busy Stratford Junction of the Grand Trunk Railroad, arranging a clock with a notched wheel to give the hourly signal which was to prove that he was awake and at his post! He left hurriedly after failing to hold a train which was nearly involved in a head-on collision. He usually worked the night shift, allowing himself time for experiments during the day. His first invention was an arrangement of two Morse registers so that a high-speed input could be decoded at a slower speed. Moving from place to place he held many positions as a telegraphist. In Boston he invented an automatic vote recorder for Congress and patented it, but the idea was rejected. This was the first of a total of 1180 patents that he was to take out during his lifetime. After six years he resigned from the Western Union Company to devote all his time to invention, his next idea being an improved ticker-tape machine for stockbrokers. He developed a duplex telegraphy system, but this was turned down by the Western Union Company. He then moved to New York.Edison found accommodation in the battery room of Law's Gold Reporting Company, sleeping in the cellar, and there his repair of a broken transmitter marked him as someone of special talents. His superior soon resigned, and he was promoted with a salary of $300 a month. Western Union paid him $40,000 for the sole rights on future improvements on the duplex telegraph, and he moved to Ward Street, Newark, New Jersey, where he employed a gathering of specialist engineers. Within a year, he married one of his employees, Mary Stilwell, when she was only 16: a daughter, Marion, was born in 1872, and two sons, Thomas and William, in 1876 and 1879, respectively.He continued to work on the automatic telegraph, a device to send out messages faster than they could be tapped out by hand: that is, over fifty words per minute or so. An earlier machine by Alexander Bain worked at up to 400 words per minute, but was not good over long distances. Edison agreed to work on improving this feature of Bain's machine for the Automatic Telegraph Company (ATC) for $40,000. He improved it to a working speed of 500 words per minute and ran a test between Washington and New York. Hoping to sell their equipment to the Post Office in Britain, ATC sent Edison to England in 1873 to negotiate. A 500-word message was to be sent from Liverpool to London every half-hour for six hours, followed by tests on 2,200 miles (3,540 km) of cable at Greenwich. Only confused results were obtained due to induction in the cable, which lay coiled in a water tank. Edison returned to New York, where he worked on his quadruplex telegraph system, tests of which proved a success between New York and Albany in December 1874. Unfortunately, simultaneous negotiation with Western Union and ATC resulted in a lawsuit.Alexander Graham Bell was granted a patent for a telephone in March 1876 while Edison was still working on the same idea. His improvements allowed the device to operate over a distance of hundreds of miles instead of only a few miles. Tests were carried out over the 106 miles (170 km) between New York and Philadelphia. Edison applied for a patent on the carbon-button transmitter in April 1877, Western Union agreeing to pay him $6,000 a year for the seventeen-year duration of the patent. In these years he was also working on the development of the electric lamp and on a duplicating machine which would make up to 3,000 copies from a stencil. In 1876–7 he moved from Newark to Menlo Park, twenty-four miles (39 km) from New York on the Pennsylvania Railway, near Elizabeth. He had bought a house there around which he built the premises that would become his "inventions factory". It was there that he began the use of his 200- page pocket notebooks, each of which lasted him about two weeks, so prolific were his ideas. When he died he left 3,400 of them filled with notes and sketches.Late in 1877 he applied for a patent for a phonograph which was granted on 19 February 1878, and by the end of the year he had formed a company to manufacture this totally new product. At the time, Edison saw the device primarily as a business aid rather than for entertainment, rather as a dictating machine. In August 1878 he was granted a British patent. In July 1878 he tried to measure the heat from the solar corona at a solar eclipse viewed from Rawlins, Wyoming, but his "tasimeter" was too sensitive.Probably his greatest achievement was "The Subdivision of the Electric Light" or the "glow bulb". He tried many materials for the filament before settling on carbon. He gave a demonstration of electric light by lighting up Menlo Park and inviting the public. Edison was, of course, faced with the problem of inventing and producing all the ancillaries which go to make up the electrical system of generation and distribution-meters, fuses, insulation, switches, cabling—even generators had to be designed and built; everything was new. He started a number of manufacturing companies to produce the various components needed.In 1881 he built the world's largest generator, which weighed 27 tons, to light 1,200 lamps at the Paris Exhibition. It was later moved to England to be used in the world's first central power station with steam engine drive at Holborn Viaduct, London. In September 1882 he started up his Pearl Street Generating Station in New York, which led to a worldwide increase in the application of electric power, particularly for lighting. At the same time as these developments, he built a 1,300yd (1,190m) electric railway at Menlo Park.On 9 August 1884 his wife died of typhoid. Using his telegraphic skills, he proposed to 19-year-old Mina Miller in Morse code while in the company of others on a train. He married her in February 1885 before buying a new house and estate at West Orange, New Jersey, building a new laboratory not far away in the Orange Valley.Edison used direct current which was limited to around 250 volts. Alternating current was largely developed by George Westinghouse and Nicola Tesla, using transformers to step up the current to a higher voltage for long-distance transmission. The use of AC gradually overtook the Edison DC system.In autumn 1888 he patented a form of cinephotography, the kinetoscope, obtaining film-stock from George Eastman. In 1893 he set up the first film studio, which was pivoted so as to catch the sun, with a hinged roof which could be raised. In 1894 kinetoscope parlours with "peep shows" were starting up in cities all over America. Competition came from the Latham Brothers with a screen-projection machine, which Edison answered with his "Vitascope", shown in New York in 1896. This showed pictures with accompanying sound, but there was some difficulty with synchronization. Edison also experimented with captions at this early date.In 1880 he filed a patent for a magnetic ore separator, the first of nearly sixty. He bought up deposits of low-grade iron ore which had been developed in the north of New Jersey. The process was a commercial success until the discovery of iron-rich ore in Minnesota rendered it uneconomic and uncompetitive. In 1898 cement rock was discovered in New Village, west of West Orange. Edison bought the land and started cement manufacture, using kilns twice the normal length and using half as much fuel to heat them as the normal type of kiln. In 1893 he met Henry Ford, who was building his second car, at an Edison convention. This started him on the development of a battery for an electric car on which he made over 9,000 experiments. In 1903 he sold his patent for wireless telegraphy "for a song" to Guglielmo Marconi.In 1910 Edison designed a prefabricated concrete house. In December 1914 fire destroyed three-quarters of the West Orange plant, but it was at once rebuilt, and with the threat of war Edison started to set up his own plants for making all the chemicals that he had previously been buying from Europe, such as carbolic acid, phenol, benzol, aniline dyes, etc. He was appointed President of the Navy Consulting Board, for whom, he said, he made some forty-five inventions, "but they were pigeonholed, every one of them". Thus did Edison find that the Navy did not take kindly to civilian interference.In 1927 he started the Edison Botanic Research Company, founded with similar investment from Ford and Firestone with the object of finding a substitute for overseas-produced rubber. In the first year he tested no fewer than 3,327 possible plants, in the second year, over 1,400, eventually developing a variety of Golden Rod which grew to 14 ft (4.3 m) in height. However, all this effort and money was wasted, due to the discovery of synthetic rubber.In October 1929 he was present at Henry Ford's opening of his Dearborn Museum to celebrate the fiftieth anniversary of the incandescent lamp, including a replica of the Menlo Park laboratory. He was awarded the Congressional Gold Medal and was elected to the American Academy of Sciences. He died in 1931 at his home, Glenmont; throughout the USA, lights were dimmed temporarily on the day of his funeral.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsMember of the American Academy of Sciences. Congressional Gold Medal.Further ReadingM.Josephson, 1951, Edison, Eyre \& Spottiswode.R.W.Clark, 1977, Edison, the Man who Made the Future, Macdonald \& Jane.IMcN -
17 plug
1) пробка; заглушка || затыкать пробкой; заглушать отверстие2) тампон || тампонировать3) закупорка; засор(ение) || закупоривать; засорять(ся)4) горн. забойка6) днище ( конвертера)7) дюбель || забивать дюбель9) набивка (напр. сальника насоса)11) пуансон ( пресс-формы)12) свеча зажигания, запальная свеча13) вилка ( электрического соединителя); штепсель; штекер14) штырь; штырёк16) амер. короткая заметка для заполнения неиспользованной части газетной полосы17) табачный штранг18) пищ. проба ( продукта), взятая щупом•to plug back — устанавливать (цементную) пробку (в скважине с целью разработки вышезалегающего коллектора)-
air-flow plug
-
aligning plug
-
angle plug
-
answering plug
-
attachment plug
-
bag plug
-
ball plug
-
banana plug
-
bleeder-style plug
-
bleeder plug
-
blind plug
-
bottom cementing plug
-
bottom plug
-
branch plug
-
bridge plug
-
bull plug
-
button plug
-
cable plug
-
calling plug
-
cannon plug
-
casing banger test plug
-
catalyst plug
-
cementing plug
-
channel closure plug
-
character width plug
-
choke plug
-
cinder plug
-
cleanout plug
-
closing cementing plug
-
cock plug
-
cold spark plug
-
cold plug
-
conical plug
-
connecting plug
-
core plug
-
corrugated wood plug
-
countersunk plug
-
cylinder head plug
-
dielectric plug
-
direction-connection plug
-
displacement plug
-
double-pin plug
-
drain plug
-
drift plug
-
drillable bridge plug
-
dry-hole plug
-
Edison screw plug
-
ejecting plug
-
end plug
-
expanding plug
-
expanding test plug
-
filler plug
-
fire plug
-
fixed plug
-
flat pin plug
-
float plug
-
floating plug
-
flush plug
-
fuel plug
-
fuse plug
-
gage plug
-
glow plug
-
ground plug
-
half-tone plug
-
hearth plug
-
heating plug
-
hinged vent plug
-
hollow axle plug
-
hot spark plug
-
hot plug
-
ice plug
-
ignition spark plug
-
ignition plug
-
inquiry plug
-
internal hex plug
-
jumper plug
-
junction cord plug
-
lamp holder plug
-
lead plug
-
limit plug
-
lubricating plug
-
magnetic plug
-
male plug
-
matching plug
-
mine survey plug
-
multiple plug
-
nailing plug
-
oil-level plug
-
open plug
-
opening cementing plug
-
orifice plug
-
out-of-service plug
-
parallel plug
-
phone plug
-
phono plug
-
piercer plug
-
pin plug
-
pipe plug
-
pneumatic plug-in port plug
-
polarity plug
-
polarized plug
-
priming plug
-
removable plug
-
retrievable bridge plug
-
rotating plug
-
safety plug
-
sand plug
-
screw plug
-
seal plug
-
self-aligned plug
-
sheathed-element glow plug
-
shielding plug
-
shield plug
-
short-circuiting plug
-
sloshing electron plug
-
snatch plug
-
socket plug
-
spark plug
-
sprue plug
-
static vent plug
-
stationary plug
-
stemming plug
-
stopper plug
-
straight plug
-
switch plug
-
tapered plug
-
telephone plug
-
terminal plug
-
Thomas plug
-
threaded plug
-
three ground spark plug
-
three-pin plug
-
top cementing plug
-
tube plug
-
tuning plug
-
tuyere plug
-
two-pin plug
-
vent plug
-
wall plug
-
water-jacket plug
-
welch plug
-
wiper plug
-
wooden peg-sleeper plug
-
wooden plug -
18 starter
1) эл. пусковое устройство, пускатель, стартер; пусковой реостат2) диспетчер3) зажигатель6) стартёр (1. устройство для пуска двигателя 2. устройство для зажигания электролюминесцентных ламп)7) забурник; короткий бур ( для начала бурения)9) пищ. закваска•-
air-turbine starter
-
automatic motor starter
-
autotransformer starter
-
cascade starter
-
closed circuit transition starter
-
closed transition starter
-
contactor starter
-
crank starter
-
direct-cranking starter
-
drum switch starter
-
drum starter
-
electric starter
-
enclosed starter
-
group starter
-
hand starter
-
hydraulic starter
-
impedance starter
-
impulse starter
-
inching starter
-
increment starter
-
inductor starter
-
inertia starter
-
lamp resistance starter
-
liquid starter
-
magnetic full-voltage starter
-
medium-voltage motor starter
-
motor starter
-
motor-driven starter
-
multiple-switch starter
-
multistep starter
-
oil starter
-
oil-cooled starter
-
on-line starter
-
open starter
-
part-winding starter
-
pole-changing starter
-
push-button starter
-
reactance starter
-
reconnection starter
-
reduced-current starter
-
reduced-voltage starter
-
relay-operated starter
-
reversing-type starter
-
rheostatic starter
-
rotor-resistance starter
-
series-parallel starter
-
slow-motion starter
-
solenoid starter
-
solid-state starter
-
star-delta starter
-
stator starter
-
straight-on starter
-
switching starter
-
switch starter
-
three-phase starter
-
transformer starter
-
turbine starter
-
water resistance starter
-
Y-delta starter -
19 carbon
1) углевод
2) карбон
3) нагар
4) нагарный
5) сажевый
6) саженаполненный
7) углекислый
8) углерод
9) углеродистый
10) углеродный
11) углоеродистый
12) угольно-дуговой
13) угольный стержень
14) сажистый
– activated carbon
– amorphous carbon
– carbide carbon
– carbon arc welding
– carbon bisulphide
– carbon boil
– carbon brush
– carbon cycle
– carbon deposit
– carbon dioxide
– carbon dust
– carbon iron
– carbon lamp
– carbon lining
– carbon microphone
– carbon monoxide
– carbon packing
– carbon paper
– carbon protector
– carbon resistor
– carbon slurry
– carbon steel
– carbon tetrachloride
– decolorizing carbon
– fixed carbon
– free carbon
– graphitic carbon
– graphitized carbon
– pyrolytic carbon
– retort carbon
– unburned carbon
carbon pressure recording — запись через копировальную бумагу
pyrolytically precipitated carbon — <chem.> пироуглерод
single-button carbon microphone — однокапсюльный угольный микрофон
-
20 switch
1) переключатель
2) включатель
3) выключатель
4) коммутационный механизм
5) переключать
6) переключение
7) шальтер
8) искатель
9) <comput.> кнопочный
10) коммутатор
11) < railways> стрелочный
12) включать
13) менять направление
14) выключать
15) переключательный
16) прут
17) штепсель
18) штепсельный
19) ключ
20) многоходовой
21) трансформаторный
– acknowledging switch
– air-break switch
– air-pressure switch
– alternate switch
– antenna switch
– antenna-ground switch
– anti-capacitance switch
– assignment switch
– at flick of switch
– automatic switch
– band switch
– barometric switch
– battery switch
– branch switch
– by-pass switch
– cam switch
– cam-operated switch
– cell switch
– challenge switch
– channel switch
– close switch
– connector switch
– control switch
– controlled switch
– cradle switch
– cross-bar switch
– crossbar switch
– crosspoint switch
– cutoff switch
– delayed-action switch
– diode switch
– door-operated switch
– double-break switch
– double-pole switch
– double-throw switch
– double-way switch
– drum switch
– earthing switch
– electronic switch
– emergency switch
– enclosed switch
– end cell switch
– end switch
– end-cell switch
– entrance switch
– explosion-proof switch
– ferrite switch
– filament switch
– finder switch
– flag switch
– flush-mounting switch
– foot switch
– forestalling switch
– four-layer switch
– function switch
– fuse switch
– gang switch
– gate-activated switch
– grounding switch
– group switch
– hand-operated switch
– high-speed switch
– horn-gap switch
– interlocked switch
– interval cam switch
– knife switch
– lever switch
– limit switch
– liquid-level switch
– mains switch
– master switch
– matrix switch
– mercury switch
– minor switch
– motor-operated switch
– multi-pole switch
– multi-position switch
– multiple switch
– multiple-contact switch
– multipole switch
– multiway switch
– nut switch
– oil-immersed switch
– on-off switch
– one-motion switch
– open switch
– oscillating switch
– outlying switch
– pendulum switch
– piano-key switch
– plug switch
– plug-in switch
– pole switch
– power switch
– power-operated switch
– proximity switch
– push-button switch
– range switch
– reed switch
– relay switch
– remote switch
– reset switch
– rocker switch
– rotary switch
– route switch
– safety switch
– sectionalizing switch
– semiconductor switch
– single-break switch
– single-pole switch
– single-way switch
– slide switch
– solenoid switch
– solenoid-operated switch
– solid-state switch
– spring-return switch
– starting switch
– static switch
– step switch
– step-by-step switch
– stepping switch
– Strowger switch
– surface switch
– switch adjustment
– switch apparatus
– switch arm
– switch board
– switch chair
– switch circuit
– switch contacts
– switch engine
– switch in use
– switch indicator
– switch key
– switch lamp
– switch off
– switch on light
– switch out of use
– switch tie
– switch tongue
– switch tower
– switch tracks
– thermal switch
– throw a switch
– throwing of a switch
– thyristor switch
– toggle switch
– transfer switch
– transistor switch
– transmit-receive switch
– two-motion switch
– vacuum switch
– voltage-selector switch
– wafer switch
– wave-range switch
azimuth stowing switch — <tech.> ключ походного положения азимутальный
field discharge switch — <electr.> автомат гашения поля
magnetically operated switch — выключатель с магнитным приводом
momentary action switch — клавишный переключатель без фиксации
move switch to OFF position — ставить выключатель в положение ВЫКЛ
move switch to ON position — ставить выключатель в положение ВКЛ
numerical connector switch — искатель с вынужденным движением
silicon bilateral switch — тиристор симметричный пороговый триодный
switch laser Q to a low value — выключать добротность лазера
switch machine lever — рукоятка управления стрелочным приводом
switch section of multiple — секция многократного поля добавочная
switch signal lever — < railways> рукоятка стрелочного указателя
trafction indicator switch — переключатель указателя поворота
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
Carbon button lamp — The carbon button lamp is a single electrode incandescent lamp invented by Nikola Tesla during his effort to get around the Edison patent for the incandescent light bulb. A carbon button lamp contains a small carbon sphere positioned in the… … Wikipedia
button — [but′ n] n. [ME botoun < OFr boton, a button, bud < buter: see BUTT2] 1. any small disk, knob, etc. used as a fastening or ornament, as one put through a buttonhole on a garment 2. anything small and shaped like a button; specif., a) a… … English World dictionary
Plasma lamp — Plasma lamps (also variously plasma globes, balls, domes, spheres, or orbs) are novelty items which were most popular in the 1980s. The plasma lamp was invented by Nikola Tesla after his experimentation with high frequency currents in an… … Wikipedia
attendant direct station selection with busy lamp — The ability to place or complete calls to stations within the PBX through the attendant console by using a nonblocking push button associated with the desired station; a light indicates whether the station is busy or idle … IT glossary of terms, acronyms and abbreviations
Light fixture — This article is about architectural light fixtures. For stage lighting, see Stage lighting instrument. Many various light fixtures A light fixture, light fitting, or luminaire is an electrical device used to create artificial light and/or… … Wikipedia
List of light sources — This is a list of sources of light, including both natural and artificial sources, and both processes and devices .Natural [ Lightning can be a spectacular source of illumination.] *Astronomical objects **Sunlight (Solar radiation)… … Wikipedia
Tesla, Nikola — born July 9/10, 1856, Smiljan, Lika, Austria Hungary died Jan. 7, 1943, New York, N.Y., U.S. Serbian U.S. inventor and researcher. He studied in Austria and Bohemia and worked in Paris before coming to the U.S. in 1884. He worked for Thomas Alva… … Universalium
GPO telephones — The United Kingdom s General Post Office (GPO) had a number of telephones that were provided by them for connection to their exchanges. Until 1982 the GPO had a monopoly on the provision of all telephones within the UK and so the range was… … Wikipedia
Dharma Initiative — Logo of the Dharma Initiative The Dharma Initiative, also written DHARMA (Department of Heuristics and Research on Material Applications[1]), was a fictional research project featured in the television series Lost. It was introduced in the second … Wikipedia
Command pattern — In object oriented programming, the command pattern is a design pattern in which an object is used to represent and encapsulate all the information needed to call a method at a later time. This information includes the method name, the object… … Wikipedia
X10 (industry standard) — X10 is an international and open industry standard for communication among electronic devices used for home automation, also known as domotics . It primarily uses power line wiring for signaling and control, where the signals involve brief radio… … Wikipedia
